Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing and Multi-Carrier Code Division Multiple Access
CHAPTER - 1
Introduction
1.1 Overview
Order custom essay Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing and Multi-Carrier Code Division Multiple Access with free plagiarism report
 450+ experts on 30 subjects
450+ experts on 30 subjects
 Starting from 3 hours delivery
Starting from 3 hours delivery
The involvement for wireless communications disposals has developed gigantically. In malice of the fact that the agreement of 3rd coevals cellular model has been slower than was ab initio expected, scientists are now analyzing 4th coevals cellular systems. These models will convey at much higher rates than the echt 2G models, and even 3G models, in an of all time jammed frequence spectrum. The indispensable aim of next-generation radio systems ( 4G ) won’t merely be the familiarity of new inventions with spread the demand for higher information rates and new services, to boot the incorporation of bing progresss in a typical phase. The scheme of multi-carrier transmittal has late been having broad involvement, peculiarly for high informations rate broadcast applications. The cardinal points of multi-carrier transmittal are its strength in frequence selective attenuation channels and specifically, the reduced signal processing complexness by equalisation in the frequence sphere.
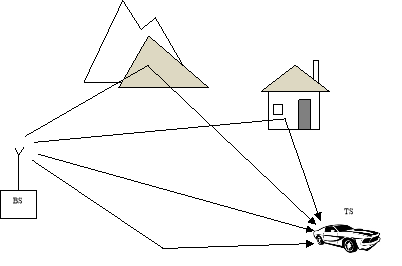
Figure 1.1: Time variant multipath extension
Signals in wireless communicating state of affairss are impaired by melting and multipath hold spread. This prompts a corruptness of the general executing of the model. Henceforth, a few techniques are accessible to relieve these damages and fulfill the expanding demands. Figure 1.1 demonstrates an illustration of clip variant multipath extension.
A considerable step of involvement has been placed in transition techniques like Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing ( OFDM ) and Code Division Multiple Access ( CDMA ) . Multiple entree strategies based on a combination of codification division and OFDM techniques have already proven to be strong campaigners for future 4G systems. A major outfall of the higher coevals radio systems is spectral efficiency.
In this study, we concentrate on Multicarrier Code-Division Multiple Access ( MCCDMA ) , a fresh digital transition and multi entree strategy. It is a promising attack to the challenge of supplying high informations rate radio communicating. MC-CDMA combines the benefits of CDMA with the natural hardiness to frequency selectivity offered by OFDM. It can be interpreted as CDMA with the distributing taking topographic point in the frequence instead than temporal sphere.
Multicarrier CDMA is merger of two different techniques:
- Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing ( OFDM )
- Code Division Multiple Access ( CDMA )
1.2 Communication System
Communication is a manner of conveying information, ’ Technology alterations, but communicating lasts’ ; the handiness of communicating engineerings has made a great impact on human lives. When we communicate, we are sharing information. This sharing can be local or distant. While distant communicating takes topographic point over a distance, the term “telecommunication” includes telephone and telecasting, means communicating at a distance ( tele is Grecian for “far” )
Telecommunications can therefore grouped into two -voice & A ; informations.
Three cardinal faculties that comprise a full communicating channel:
The Sender – A sender encodes the message in a linguistic communication that can be understood by the receiving system.
- The Receiver –decodes the message.
- The Medium – Air, Cu wires, optical fibre. These carry the message across from the transmitter to the receiving system.
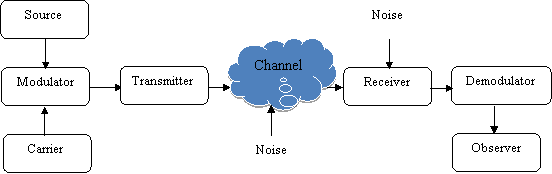
Figure 1.2: Communication system
Telecommunication systems have now made it possible to pass on with virtually anyone at any clip. Early telegraph and telephone system used Cu wire to transport signals over the earth’ surface and across oceans and high frequence ( HF ) wireless, besides normally called shortwave wireless, made possible intercontinental telephone links.
But now there is different types of communicating strategy. They are following:
- Telephone System
- Cellular Systems
- Packet Data Systems
- Satellite Systems
- Microwave Systems
- Fiber Optic Systems
Every communicating system has its ain frequence scope, system, capacity, application execution cost.
On the footing of transmittal system there are two types of communicating system
- Wired communicating system
- Wireless communicating system
1.2.1 Wireless Communication
It is the transportation of information over a distance without the usage of electrical music directors or “wires” The distances involved may be short agencies few metres as in telecasting remote control or long like 1000s or 1000000s of kilometres for wireless communications. When the scene is clear, the period is frequently shortened to “wireless” . Wireless communicating is by and large considered to be a subdivision of telecommunications. The term “wireless” has become a generic and across-the-board word used to depict communications in which electromagnetic moving ridges or RF ( instead than some signifier of wire ) carries a signal over portion or the full communicating way.
1.2.2 Previous Work on Wireless System
Jagadish Chandra Bose has been credited with the innovation of the first radio sensing device and the find of millimetre length electromagnetic moving ridges. David E. Hughes, eight old ages before Hertz’s investigates, induced electromagnetic moving ridges in a signaling system. Hughes base on balls on Morse codification by an initiation device. In 1878, Hughes’s initiation transmittal strategy utilized a “clockwork transmitter” to convey signals. In 1885, T. A. Edison used a vibrator magnet for initiation transmittal. In 1888, Edison set up a theoretical account of signaling on the Lehigh Valley Railroad. In the history of radio engineering, the presentation of the theory of electromagnetic moving ridges by Heinrich Rudolf Hertz in 1888 was of import. The theories of electromagnetic moving ridges were predicted from the research of James Clerk Maxwell and Michael Faraday. Hertz established that electromagnetic moving ridges could be transmitted and caused to go through infinite in consecutive lines and that they were able to be received by an investigational tool. The research was non followed up by Hertz. The applied utilizations of the radio communicating and remote control engineering were implemented by Nikola Tesla.
1.3 Drawbacks of Communication System
Communication system has some restriction. Bandwidth and Noise restriction is portion of the communicating system. Bandwidth is merely a step of frequence scope. It is easy to see that the bandwidth we define here is closely related to the sum of informations you can convey within it, therefore the more infinite in the frequence spectrum, the more informations you can suit in at a given minute.
In a communications system deficiency of bandwidth means deficiency of throughput of apprehensible informations. So that Bandwidth restriction means curtailing the measure of information transmitted from transmitter to receiver each 2nd. The consequences of which are the debasement in the quality of information arrives.
Noise will besides impact intelligibility. In an electronic device such as an operational amplifier so there is such a thing known as a addition bandwidth merchandise, in other words how fast can the end product respondent to the input and how much crud ( noise ) is added in the procedure. Thermal noise is besides a topic and Boltzmann’s changeless K finds its manner into the figure of equations. The noise is so important, a assortment of steps have been developed to quantify the consequence of noise in a communications system There is another restriction of communicating is melting. Fading is the fluctuation happened in standard signal strength at the receiving system that is, any arbitrary divergence in the standard signal can be named as attenuation. However the microwave signal travel in the medium due to different parametric quantities there is a decrease in signal strength.
1.4 Multiple Access Methods
A limited sum of bandwidth is allocated for radio services. A wireless theoretical account is compulsory to suit as many users as possible by efficaciously apportion the bandwidth. Therefore, in the field of communications, the word multiple entree could be chiseled as a manner of leting multiple users to concurrently administer the finite bandwidth with smallest likely debasement in the public presentation of the system. There are a figure of methods demoing how the multiple accessing can be attained. There are four basic strategies:
- Frequency Division Multiple Access ( FDMA ) .
- Time Division Multiple Access ( TDMA ) .
- Code Division Multiple Access ( CDMA )
- Space Division Multiple Access ( SDMA )
These techniques can be grouped as wideband and narrowband systems, subjected to how the available bandwidth is allocated to the users. The duplexing method of a multiple entree system is normally described along with the peculiar multiple entree system, as shown in the cases that follow.
Narrowband Systems:The term narrowband is used to associate the bandwidth of a individual channel to the expected coherency bandwidth of the channel. In a narrowband multiple entree strategy, the unfilled wireless spectrum is separated into a big figure of narrowband channels. The channels are by and large operated utilizing FDD. To diminish intervention between contrary and frontward links on each channel, the frequence separation is made every bit great as possible within the frequence spectrum, while still allowing low-priced duplexers and a common transceiver aerial to be used in each subscriber terminal.
Wideband Systems:In wideband theoretical accounts, transmittal bandwidth of a individual channel is much larger than the coherency bandwidth of the channel. Therefore, multi-path attenuation does non greatly vary the standard signal power within a wideband channel and the frequence selective slices go on in merely a little fraction of the signal bandwidth at any juncture of clip. In wideband multiple entree theoretical accounts a big figure of senders are allowed to convey on the same channel.
1.5 Requirement of MC-CDMA
Three major multiple entree strategies exist: frequence division multiple entree ( FDMA ) , clip division multiple entree ( TDMA ) and code division multiple entree ( CDMA ) [ 1 ] . In the undermentioned subdivisions, the advantages and disadvantages of these techniques will be studied, and the necessity for multicarrier codification division entree ( MC-CDMA ) will be discussed.
1.5.1 Frequency Division Multiple Access ( FDMA )
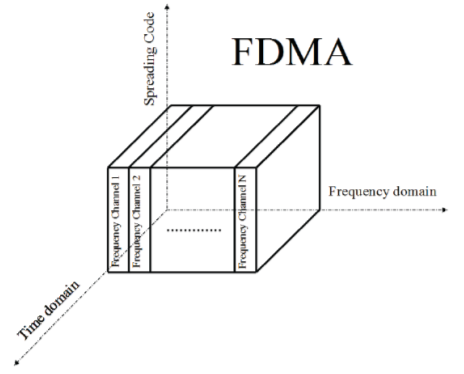
Figure 1.3: Frequency division multiple entree ( FDMA ) [ 1 ]
Frequency division multiple entree ( FDMA ) was the first multiple entree technique, developed in the early 1900s [ 2 ] . With FDMA, the entire frequence bandwidth is divided into frequence channels that are assigned to each user for good, ensuing in multiple user signals that are both spectrally separated and at the same time transmitted and received. This has been diagrammatically signified in Figure 1.3.
The FDMA systems require a comparatively simple algorithm and execution compared to TDMA and CDMA [ 1 ] , but there are several drawbacks. First, due to the lasting assignment of FDMA channels, fresh channels can non be utilized by other clients, the effect of which is the abuse of the communicating resources. Second, nonlinearities in the power amplifier can do signal spreading in the frequence sphere, doing inter-channel intervention ( ICI ) in other FDMA channels. Finally, the capacity of an FDMA system is limited by Thursday vitamin E figure of channels available.
1.5.2 Time Division Multiple Access ( TDMA )
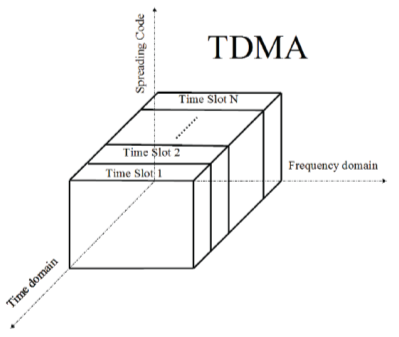
Figure 1.4: Time division multiple entree ( TDMA ) [ 1 ]
Time division multiple entree ( TDMA ) has been developed with a similar thought to FDMA, but with TDMA, multiple user signals are separated in the clip sphere instead than the frequence sphere. Figure 1.4 shows a TDMA system with the transmittal clip divided into a figure of cyclically reiterating clip slots that can be assigned to single users, leting all users entree to all of the available bandwidth.
Compared to FDMA systems, TDMA systems offer more flexibleness in the assignment of clip slots whereby different Numberss of clip slots can be allocated to different users depending on the service needed. In add-on, because TDMA users can convey signals merely in their ain clip slots, the transmittal of TDMA signal is noncontiguous and occurs in explosions, ensuing in less battery power ingestion. But, the TDMA signal needs a big synchronism operating expense due to its non-continuous transmittal. Inter-symbol intervention ( ISI ) , caused by multipath extension, is besides a serious bug for TDMA, particularly durin g high informations rate transmittals.
1.5.3 Code Division Multiple Access ( CDMA )
In the last 10 old ages, codification division multiple entree ( CDMA ) has been developed to get the better of the disadvantages of other multiple entree techniques such as TDMA and FDMA [ 3 ] .
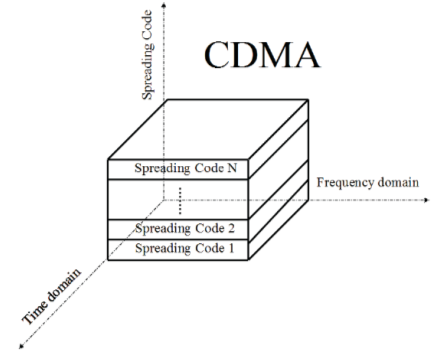
Figure 1.5: Code division multiple entree ( CDMA ) [ 1 ]
Figure 1.5 demonstrates multiple CDMA user signals that are separated by distributing sequences. In specific, all user signal is spread utilizing a pseudorandom sequence which is extraneous to the sequence of other users. As a consequence, merely the intended user-receiver can despread and have the information right ; other users on the system perceive the signal as noise, ensuing in multiple user signals that can be transmitted within the same bandwidth at the same time. The chief advantage with CDMA is that the system capacity is limited merely by the sum of intervention ; with a lower degree of intervention the system can back up a higher figure of users [ 1 ] . CDMA systems are besides robust to narrow set jamming as the receiver signal can distribute the jamming signal’s energy over the full bandwidth doing it undistinguished in comparing to the signal itself [ 2 ] . If the spreading sequence is absolutely extraneous, it is possible to convey multiple CDMA signals without presenting multiple entree intervention ( MAI ) during synchronal transmittal [ 3 ]
Assorted types of CDMA such as direct-sequence CDMA ( DS-CDMA ) and wideband CDMA ( W-CDMA ) , have been utilised and advanced in both 2G and 3G systems similar to CDMA One ( IS-95 ) , UMTS and CDMA2000 [ 4 ] . These techniques are considered to be single-carrier CDMA systems. Unfortunately when traveling into the 4th coevals of wireless communicating systems ( 4G ) , in which information is transmitted at a rate every bit high as 1 Giga bits-per-second ( bits per second ) [ 5 ] , single-carrier CDMA theoretical accounts are non appropriate. This is for the grounds as fallow
- With high informations rates the symbol continuance will go sawed-off, ensuing in the channel hold spread transcending the symbol continuance doing ISI [ 6 ] .
- When informations rate goes beyond a 100 Mega bits per second, it turn out to be a hard undertaking to synchronise, as the information is sequenced at high velocities [ 7 ] .
- Because of the multipath extension, signal energy is distributed in the clip sphere: in single-carrier CDMA systems such as DS-CDMA, RAKE receiving systems are frequently used to unite the multipath signals. However, non all waies of signals can be successfully received. If the figure of fingers in the RAKE receiving system is less than the figure of resolvable waies, some of the standard signal energy can non be combined, therefore a part of the signal energy is lost [ 8 ] . But if the figure of fingers in the RAKE receiving system is more than the figure of resolvable waies, noise will be improved.
Therefore an Orthodox single-carrier CDMA such as DS-CDMA is non practical for 4G systems where a high information rate is required.
1.5.4 Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing ( OFDM )
Orthogonal frequence division multiplexing ( OFDM ) proposed in [ 9 ] has the ability to back up higher information rate transmittal. When utilizing OFDM, the channel bandwidth is divided into a figure of equal bandwidth bomber channels, with each bomber channel using a subcarrier to convey a information symbol. The frequence separation of next subcarriers is chosen to be the opposite of the symbol continuance, ensuing in all the subcarriers being extraneous to one another over one symbol interval. Therefore, OFDM method can convey a immense figure of different informations symbols over multiple subcarriers at the same time, enabling this technique to back up a higher information rate transmittal. In add-on the bandwidth of each bomber channel is designed to be so narrow that the frequence features of each bomber channel are changeless, creative activity OFDM signals healthy to frequency selective attenuation [ 10 ] . The other advantage of OFDM is that the signal can be easy and expeditiously modulated and demodulated utilizing fast Fourier transform ( FFT ) devices [ 11 ] . As FFT can be easy implemented, the receiving system complexness does non increase well while transmittal rate can be mostly increased.
Despite all these advantages, OFDM still has some drawbacks due to its execution of multicarrier transition. OFDM suffers a high peak-to-average power ratio that occurs when all the signals in the subcarriers are added constructively [ 12, 13 ] . This consequences in the impregnation of the power elaboration at the sender, triping inter-modulation deformation. OFDM is really sensitive to frequency offset, as the graph of the subcarriers is overlapping [ 14, 15 ] . Any frequence offset can do to ICI, which put forward that OFDM requires a high grade of synchronism of subcarriers. Besides, the conventional OFDM systems can back up merely a individual client, demanding the demand for multicarrier codification divi Zion multiple entree ( MC-CDMA ) .
1.5.5 Multicarrier Code Division Multiple Access ( MC-CDMA )
Based on the combination of OFDM and DS-CDMA, a multicarrier codification division multiple entree ( MC-CDMA ) is proposed [ 16 ] . Unlike DS-CDMA, which spreads the original information watercourse into the clip sphere, MC-CDMA spreads the original information watercourse into the frequence sphere by ab initio change overing the input informations watercourse from consecutive to parallel so multiplying this watercourse by the distributing french friess in different OFDM subcarriers, the consequence of which is MC-CDMA signal which takes on the advantages of both DS-CDMA and OFDM. The advantages of MC-CDMA are:
- The capacity is interference limited [ 17 ] and any techniques that cut down intervention are capable of increasing the capacity of MC-CDMA.
- The signal is robust to frequency selective attenuation and can back up high informations rate transmittal.
- Bandwidth is used more expeditiously as the spectra of subcarrier convergence [ 18 ] .
- Since the standard signal is combined in the frequence sphere, an MC-CDMA receiving system can use all the standard signal energy scattered in the frequence sphere [ 19 ] . This is a important advantage over DS-CDMA, where portion of the signal energy can be lost due to deficient figure of fingers in the RAKE receiving system.
- The sender and receiving system signals can be implemented utilizing FFT, which does non increase the grade of complexness.
1.6 Objective
The chief aim of this thesis is to develop an attack to minimise the consequence of multipath attenuation in Rayleigh attenuation environment utilizing Multicarrier CDMA ( MC-CDMA ) with RAKE receiving system and different uniting strategies viz ; Equal Gain Combining ( EGC ) , Maximal Ratio Combining ( MRC ) , Zero-Forcing ( Z-F ) and Minimal Mean Square Error ( MMSE ) Equalization.
1.7 Outline Of Dissertation
Chapter-1 Introduction: This chapter is divided in six parts ; overview, communicating system, drawbacks of communicating system, multiple entree methods, demand of MC-CDMA, and eventually nonsubjective is explained.
Chapter-2 Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing: This chapter gives a elaborate account about overview of OFDM, guard interval, perpendicularity, mathematical analysis of OFDM and fourier transform.
Chapter-3 Multi-Carrier Code Division Multiple Access: This chapter gives elaborate information about overview of multi-carrier transition, channel synchronism and appraisal in multi-carrier systems, overview of CDMA, rudimentss of MC-CDMA and channel theoretical accounts.
Chapter-4 Literature Review: This chapter gives elaborate information about old work on Multi Carrier Code Division Multiple Access. It besides elaborate the job definition sing the research work.
Chapter-5Proposed Methodology: This chapter explains the proposed methodological analysis which is used in this undertaking.
Chapter-6Simulation Consequence: This chapter shows the simulation consequences of the proposed work.
Chapter-7Conclusion and Future Scope: This chapter summarizes the parts of the thesis.
1
Cite this Page
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing and Multi-Carrier Code Division Multiple Access. (2018, Aug 26). Retrieved from https://phdessay.com/orthogonal-frequency-division-multiplexing-and-multi-carrier-code-division-multiple-access/
Run a free check or have your essay done for you


