Accounting Cycle Steps
The Accounting Cycle is a combination of processes that occurs at various periods throughout a designated time period. The time period can be weekly, monthly, quarterly, semi-annually, or annually, based on the needs of the organization or company for which the accounting cycle is being performed for. The cycle consists of ten steps.
The nine steps of Accounting Steps:
Order custom essay Accounting Cycle Steps with free plagiarism report
 450+ experts on 30 subjects
450+ experts on 30 subjects
 Starting from 3 hours delivery
Starting from 3 hours delivery
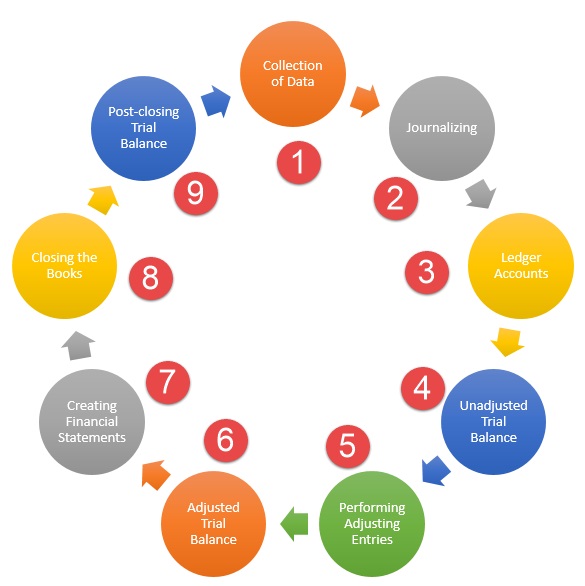
- 1 Step - Collection of Data
- 2 Step - Journalizing
- 3 Step - Ledger Accounts
- 4 Step - Unadjusted Trial Balance
- 5 Step - Perfoming Adjusting Entries
- 6 Step - Adjusted Trial Balance
- 7 Step - Creating Financial Statements
- 8 Step - Closing the Books
- 9 Step - Post-Closing Trial Balance
What are the steps in the accounting cycle?
The steps are as follows: Step one refers to analyzing transactions. Step two consists of journalizing. Step three is posting. Step four is preparing an unadjusted trial balance. Step five is adjusting. Step six consists of preparing an adjusted trial balance. Step seven is preparing financial statements. Step eight is to close. Step nine is to prepare a post-closing trial balance, and step ten is to reverse. This paper will further discuss the accounting cycle, the effects of omissions, and finish with an overview of financial statements.
The accounting cycle was originally designed for accountants that did not have access to the computer software we do today. A lot of the accounting software programs available allow users to complete a variety of the accounting cycle steps in one step, or to accomplish the steps somewhat out of order. The basis for which these steps were designed, however, has not changed. This is the primary reason which financial professionals and students focusing their studies in anything business related still learn the accounting cycle. Analyzing transactions means that a company must save all purchase documents, checks, receipts, and any other document which would indicate a financial transaction.
To journalize the transactions, one must determine which accounts will be affected by the transaction and correctly record the transaction to reflect those accounts. The accountant must use double entry method of accounting in journalizing the transactions. The purpose of preparing the various trial balances to is to double check how accurate the results are coming out with the figures entered. There are various checks and balances in accounting to ensure accuracy in reporting. The purpose of making correcting entries and reversing entries is so that all numbers and figures balance out correctly to ensure transparency in the financial figures of a company.
If an individual skips a step or leaves a step out inadvertently, the data may not be accurate or may be missing key components. In order to have the most accurate balances and most transparent financial data, steps must not be omitted. The omission of steps may potentially lead to inaccuracies as well as quantitative discrepancies that could eventually lead to poor standards of performance, a failed audit, or even litigation. All stakeholders in a company look at the financial statements of a company in order to assess a company's health. If an accounting step or figure is not accurately reported, the stakeholders, such as the executives, the customers, or the owners may not make the decisions that are best for the company.
Some of the major financial statements that come out of the accounting cycle are the balance sheet, the cash flow statement, the income statement, and the shareholders equity statement. These statements are all important in that they have various purposes for the company. They show the money coming in and going out in order to evaluate profits, sales, expenses, and other factors which a company may choose to change in order to become more effective and efficient. In order for a company to be successful and profitable, they must be able to assess their financial health. These statements are also necessary to receive funding and to continue business. If the accounting cycle is not followed and strictly adhered to, these statements are sure to suffer.
The accounting cycle consists of ten steps, and must be strictly followed. If the accounting cycle is not followed, this may result in missed journal entries, ineffective reconciliations, incorrect trial balances, missed income and expenses, and an erroneous balance sheet. If the wrong balance is being reported, this may result in over spending, missed opportunities, and potential litigation in the long term. Based on the accounting cycle, the financial statements of a company are created, such as the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement.
References
Chari, V. V., Kehoe, P.J., & McGrattan, E. R. (2007). Business cycle accounting. Econometrica, 75(3), 781-836.
Related Questions
on Accounting Cycle Steps
Cite this Page
Accounting Cycle Steps. (2017, May 21). Retrieved from https://phdessay.com/he-nine-steps-o-the-accounting-cycle/
Run a free check or have your essay done for you


