Trade in the 19th-21st Century
Introduction
Explain how the function of the Mercanti
lism pattern between 1500-to the late 1700s century has influenced the International Trade Theories in the 19
-
21
st
century. ( one page ).
Order custom essay Trade in the 19th-21st Century with free plagiarism report
 450+ experts on 30 subjects
450+ experts on 30 subjects
 Starting from 3 hours delivery
Starting from 3 hours delivery
“Mercantilism”
A school of an economic idea developed in 16th-and 17th-century England, the mercantile system argued that a state's primary economic aim should be the accomplishment of a trade excess with the associated influx of gold. The cardinal thought was that trade was a zero-sum game and that a state could accumulate gold through a balance-of-trade excess merely at the disbursal of another state. Mercantilism had really of import influence to the organisation of Britain’s trade with other states, particularly with its settlements. And there was an assortment of rules for illustration, curtailing to provide the natural stuff for Britain’s mill and prohibiting competed with some sorts of goods. The intent of the mercantile system is to advance the economic strength of the female parent state and acquire a trade excess. However, Adam Smith thought that the mercantile system is incorrect. He believed free trade policy was better than the mercantile system. In add-on to David Hume wrote essay `` Of the Balance of Trade '' ( 1752 ) suggestion that the balance of trade excess would take to domestic monetary value degree unstable. And, he developed an early measure theory of money. In the mid- 18Thursdaycentury, hence, the mercantile system had been proved unreasonable and was replaced by the theory of comparative advantage and the industry benefits from free trade that developed by David Ricardo. In the 1840s, Mercantilism was eliminated and free trade and comparative advantage as the new economic policy for the economic system.
Although free trade had become the chiefly theory in the economic system, protectionist policies returned because of the economic catastrophe in the 1930s. Even Keynes believed that increasing the money supply could better domestic goods. Therefore the mercantile system had new followings and so-called “Neomercantilism”. Particularly in the 1940 period East Asia, Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan - and in the 1990s and early twenty-first century, China - had taken the policies of "neo-mercantilist". That enabled the East Asiatic economic systems to acquire quickly growing over a long period which impacted many other developing states, for illustration, Latin America, to take the same economic policies " neo-mercantilist".
Examine why states engage in trade and
the benefits of specialisation and trade between states.
Nowadays, international trade plays a polar function in maintaining economic addition. People the universe over have profited tremendously from the cooperation across it, for illustration, developed states get inexpensive labour and big market, and developing states get engineering and increasing populating standing. It is a win-win state of affairs. There is an assortment of benefits for both states in footings of economic and societal advancement. For economic system, particularly for free trade, there are many states benefits from this economic policy such as Latin American state, Brazil, Chile, where fiscal and free trade has quickly change their economic system. First, free trade could better the life standing of domestic citizens. Several surveys have indicated successful trade could enable people out of poorness. Through free trade, by constructing an unfastened market, could profit for the local economy because of the finances of international investing and trade. And there is possible chances to construct new industries and pull new engineerings. In add-on to which could make employee changes. Second, free trade besides can make a more competitive environment which really of import for development of domestic economic system for case China, duty rate “highest value over the past 19 old ages was 40.75 in 1992, while its lowest value was 7.69 in 2010.” During 18 old ages developing, the GDP of China had addition quickly.
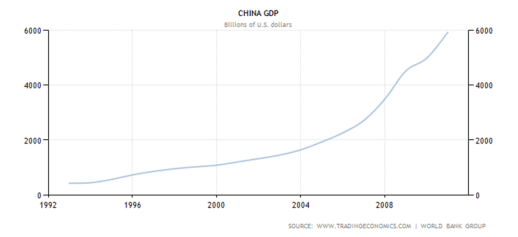
Of class, the increasing of GDP in China is the consequence of many factors while diminishing the duty rate and the barriers of import play a cardinal function for it. In fact, the political ground non merely find the economic system but besides the populating criterion of people. For societal advancement, by free trade, in one regard which can increase the finances for society, in another regard, the authorities can utilize the finances to put substructure and instruction. Equally far as we know, societal advancement should establish fiscal development.
When you sit down for your eventide repast attempt to gauge the figure of people and
minutess
that
are required to convey your repast to you-be as sidelong inventive and every bit specific as possible.
Tonight, my flushing repast was rice and fish which made by myself. For rice, purchase it from the supermarket, which is imported from Thailand. In Thailand, the rice need factors of merchandises to bring forth, which include husbandman, seeds, land and capital goods. First, husbandmen need to purchase seeds from the retail of seed and capital goods, in this measure, the store needs staff to sell the seeds and capital goods. During the period clip, the rice is produced which need to present to a factory to treat and pack and so sell to the wholesaler. Second, the employee of the council would oversee the quality of rice whether to fulfil the nutrient criterion. A wholesaler needs staff to sell the rice to retail and supermarket. In the last measure, supermarket, need staff for illustration teller to sell the rice.
For fish, it was imported from Australia. The first measure, catching the fishes in the ocean. During this procedure, need person drive the boat and staff to catch the fishes. The second measure, presenting the fish to the mill. In this measure, the mill needs staff to treat the fish and packing. A third measure, export the fish to New Zealand, in this measure, the staff of imposts would oversee the quality of the fish. The fourth measure, selling the fishes to the retail and the supermarket. And in this measure, need a driver to transport the fish to supermarket. The last measure, in the supermarket, merely like rice, need staff to shop and sell the fish. I cooked the rice and fish by the electric cooker. For the electric cooker, I think that more complicated than rice and fish. The first measure, the mill demand to by the constituent which the made by natural stuff, for illustration, plastic and metal. Both natural kinds of stuff need to delve from land, in this procedure, need tons of people to make it. In the 2nd measure, doing the natural stuff into constituents. The 3rd measure, selling and presenting the constituents to the mills that make the electric cooker. The fourth measure, the staff of the mill industry the electric cooker. The 5th measure, selling and presenting the merchandises to the retail and supermarket. It seems that is a really simple eventide repast, but behind it, there are many people to work and bring forth, which is the amazing of trade and economic. And the most of import portion of the procedure, making many changes and finances. And it is power for the development of society.
Q2
Trade construction of your chosen states
Analysis
Australia is an Oceanian state consisting the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and legion smaller islands ( Australia, en.wikipedia.org ), in the South hemisphere. New Zealand is in the South hemisphere every bit good, hence, both states have similar clime and agribusiness construction. However, the land country of Australia is 7,692,024 sq.km. larger than New Zealand land country 268021 sq.km. about 29 times. Australia’s GDP is 1560.60 USD, one million million. New Zealand’s GDP is 182.59 USD, one million million, in 2013, about 8.6 times. Australia is an affluent state; it generates its income from assorted beginnings including mining-related exports, telecommunications, banking and fabrication. ( Australia, en.wikipedia.org ) . Because of affluent mineral resource particularly iron mine in Australia, hence mining-related exports has a big proportion in its export. And she has really closely economic relation with China, every twelvemonth, China would import big Numberss of Fe mine signifier Australia.
Turn to New Zealand, because of the land country is little and low population lead to domestic consume does non-plenty, hence, international trade of New Zealand is really of import in its economic construction, peculiarly for agricultural merchandises. Exports have a big proportion that is 24 per centum of its end product, which doing New Zealand vulnerable to international goods monetary values and planetary economic. And, because of agribusiness land is affluent so, the nutrient merchandises is the most important portion of its exports in 2014, doing up 55 % of the value. Because of the affluent forest resource, Wood is the 2nd largest merchandises ( 7 % ) in New Zealand. New Zealand is good to know because of the film The Lord Of Rings and its beautiful environment. Therefore Tourism plays an important function in New Zealand's economic system, lending $ 15.0 billion to New Zealand’s entire GDP and back uping 9.6 per centum of the entire workforce in 2010. Every twelvemonth, there are tons of international visitants to New Zealand to see the astonishing landscape, and the figure of visitants are expected to increase at 2.5 per centum yearly up to 2015. Therefore, the service industry is the largest industry in the New Zealand economic system, the 2nd one is fabricating and building and so farming and natural stuff.
Data tabular array
Data tabular array must include the undermentioned information in 2013:
Table 1:
Basic economic indexes and trade construction of state Australia and New Zealand in 2013
| Australia | New Zealand | ||
| Land country ( sq.km. ) | 7,692,024 | Land country ( sq.km ) | 268021 |
| GDP ( current USD, one million millions ) | 1560.60 | GDP ( current USD, one million millions ) | 182.59 |
| GNI per capita ( current USD ) | 43084.90 | GNI per capita ( current USD ) | 32768 |
| Entire Trade ( X+M ) ( current USD, 1000000s ) | -661 | Entire Trade ( X+M ) ( current USD, 1000000s ) | 473 |
| Entire exports ( current USD, 1000000s ) | 10484 | Entire exports ( current USD, 1000000s ) | 3969 |
| Entire Import ( current USD, 1000000s ) | 11145 | Entire Import ( current USD, 1000000s ) | 3223 |
| Trade to GDP ratio I?? % I?‰ | 0.04 | Trade to GDP ratio I?? % I?‰ | 0.26 |
| Share of exports ( % ) | |||
| Agricultural Merchandises | Agricultural Merchandises | ||
| Fuels and excavation merchandises | Fuels and excavation merchandises | ||
| Industries | Industries | ||
| Share of Imports ( % ) | |||
| Agricultural Merchandises | Agricultural Merchandises | ||
| Fuels and excavation merchandises | Fuels and excavation merchandises | ||
| Industries | Industries |
Q3
Explain the theory
Analysis of absolute advantage of Australia and New Zealand
Absolute advantage is a state is said to hold an absolute advantage over another state in the production of a good or service if it can bring forth that good or service ( the ‘‘output’’ ) utilizing fewer existent resources ( like capital or labour, the ‘‘inputs’’ ). Equivalently, utilizing the same inputs, the state can bring forth more end product. To better the rule of absolute advantage, premise that there are two states (Australia and New Zealand ) bring forthing four agribusiness merchandises ( Meat, poulet, wheat, soya beans and tomatoes ), and the labour is the lone factors of merchandises. Suppose that merchandises for illustration, soya beans can be traded without costs and labours are stable in the two states. All employee in Australia or New Zealand has the same production. However, production engineering in Australia different from that in New Zealand. Suppose that Australia requires four units of labour to bring forth one unit of wheat, nevertheless the New Zealand requires merely need three units of labour. As the same as above, Australia merely needs five units of labour to bring forth one unit of tomatoes, while New Zealand needs seven units of the employee. Because Australia is more efficient to bring forth tomatoes and New Zealand is more efficient to bring forth wheat. So, there is a decision, Australia has an absolute advantage to bring forth tomatoes and New Zealand has an absolute advantage to bring forth wheat.
Because of absolute advantage that enable both states to gain advantages in trading. And this is why there is a tendency specialisation of production in the planetary economic system. Just reference above in illustration premise that Australia produces less wheat than New Zealand. If Australia frees up several units of labour from wheat to bring forth tomatoes, hence, Australia can now to bring forth more units of tomatoes ( chance cost of wheat production in Australia ). Australia has now produced less wheat and more unite tomatoes. If the premise that Australia still needs to devour the same units of wheat as earlier. It must import more wheat from New Zealand. To bring forth wheat New Zealand needs more units of the employee. This employee should come from the tomatoes industry, therefore the production of tomatoes in New Zealand will drop. ( chance costs of tomatoes production in New Zealand ) . At last, the entire production of wheat keeps the same, while the entire production of tomatoes has increased. These excess units of tomatoes are the additions from specialisation if both states focus on the products that they produce most expeditiously. This is a win-win state of affairs.
Data Table
Data tabular array must include the undermentioned information in 2013 0r 2014
Production: Four selected agricultural merchandises of India and Hungary in 2013 or 2014
| Australia | New Zealand | ||||
| Merchandise | Entire production ( tone ) | Output ( kg/hectare ) | Entire production ( tone ) | Output ( kg/hectare ) | |
| Pistachios | Pistachios | ||||
| Almonds | Almonds | ||||
| Bananas | Bananas | ||||
| Cassava | Cassava |
Q4 Comparative advantage
Explain the Theory
Application and Analysis of comparative advantage of Australia and New Zealand
The theory of comparative advantage is an economic theory about the possible additions from trade for persons, houses, or states that arise from differences in their factor gifts or technological advancement. There are two states in the information tabular array, Australia and New Zealand, which produce four agribusiness merchandises chicken, wheat, soya beans and tomatoes. To exemplify the theory merely choose two merchandises. For illustration, in Australia, it can bring forth by utilizing 10 units of labour to bring forth, or bring forth 4/5 units. And, in New Zealand could bring forth one unit by utilizing 9 units of labour, or bring forth 5/4 units. Therefore, New Zealand has an absolute advantage to bring forthing because of fewer units of labour, while Australia has a comparative advantage because of lower chance cost. Suppose that absence of trade between two states, Australia need 20 units of labours to bring forth one unit and one unit, meanwhile, New Zealand needs 17 unites to bring forth the same units. If each state focal point on the agribusiness which it has a comparative advantage, the consequence is both merchandises increases, for Australia can pass all units of labour to bring forth and New Zealand can pass all units to bring forth. So, the entire merchandise measures in addition. And base on the free trade, both states exchange one unit and one unit. Except consume the same units merchandise as earlier, there still staying more units of merchandises.
Data Table
Data tabular array must include the undermentioned information in 2013 0r 2014
Production: Four selected agricultural merchandises of India and Hungary in 2013 or 2014
| India | Hungary | ||
| Merchandise | Price per unit, USD | ||
| Pistachios | Pistachios | ||
| Almonds | Almonds | ||
| Bananas | Bananas | ||
| Cassava | Cassava |
Q5 Factor gift, trade and income distribution
- Hecksher-Ohlin ( H-O ) theoretical account
Explain the Theory
Application and Analysis of H-O theoretical account for India and Hungary Data tabular array
Data tabular array must include the undermentioned information in 2013
Factor gift and form of trade of India and Hungary in 2013 or 2014
| India | Hungary | ||
| Factors | Factors | ||
| Agricultural Land ( million hectares ) | Agricultural Land ( million hectares ) | ||
| Agricultural Land ( % of land country | Agricultural Land ( % of land country | ||
| Labour ( 1000000s ) | Labour ( 1000000s ) | ||
| Capital ( UDS, 1000000s ) | Capital ( UDS, 1000000s ) | ||
| Four major exported Merchandises | Four major exported Merchandises | Four major exported Merchandises | Four major exported Merchandises |
| Pistachios | Pistachios | ||
| Almonds | Almonds | ||
| Bananas | Bananas | ||
| Cassava | Cassava |
- Stolper-Samuelson ( S-S ) theoretical account
Explain the theory
Application and Analysis of S-S theoretical account for India and Hungary
The student should utilize information old informations tabular array to reply to this portion.
Q6 Context of new trade theories
- Economic of Scale
Explain the theory
Application and Analysis of economic of the graduated table for India and Hungary
Data tabular array
Data tabular array must include the undermentioned information in 2013 0r 2014
Domestic ingestion and export: Four selected agricultural merchandises of India and Hungary in 2013 or 2014
| India | Hungary | ||||
| Merchandise | Domestic ingestion ( tone ) | Exports ( tone ) | Domestic ingestion ( tone ) | Exports ( tone ) | |
| Pistachios | Pistachios | ||||
| Almonds | Almonds | ||||
| Bananas | Bananas | ||||
| Cassava | Cassava |
- Imperfect competition and market power
Explain the theory
Application and Analysis of imperfect competition and market power of four top bring forthing states on one selected agricultural merchandise
Data tabular array
Data tabular array must include the undermentioned information in 2013
One selected agricultural merchandise in 2013 or 2014
| Agricultural merchandise name: | ||
| Top four producing/exporting states | The volume of production ( tone ) | Share of universe production ( % ) |
| Merchandise | ||
| Pistachios | ||
| Almonds | ||
| Bananas | ||
| Cassava |
Reference
- Bowles, Paul. ( 2009 ) .The Princeton Encyclopedia of the World Economy: Essays from the Business And Economics -- Economic Situation And Conditions, ( pp.757-759 ). Princeton, Princeton University Press.
- Van M., Charles. ( 2009 ) . Absolute advantage: Essays from the Business And Economics -- Economic Situation And Conditions, ( pp.1-3 ). Princeton, Princeton University Press.
- World Trade Organization. ( 2015 ) . Retrieved from 1 April 2015, from Wikipedia:
- Hypertext transfer protocol: //en.wikipedia.org/wiki/World_Trade_Organization
- China - Duty rate. Retrieved from hypertext transfer protocol: //www.indexmundi.com/facts/china/tariff-rate
- Australia. ( 2015 ) . Retrieved from 28 April 2015, from Wikipedia
- Hypertext transfer protocol: //en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Australia
- New Zealand. ( 2015 ) . Retrieved from 28 April 2015, from Wikipedia
- Hypertext transfer protocol: //en.wikipedia.org/wiki/New_Zealand # Economy
- Comparative advantage. ( 2015 ) . Retrieved from 11 April 2015, from Wikipedia
- Hypertext transfer protocol: //en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Comparative_advantage # Ricardo.27s_example
Cite this Page
Trade in the 19th-21st Century. (2018, Aug 25). Retrieved from https://phdessay.com/trade-in-the-19th-21st-century/
Run a free check or have your essay done for you


